Carbohydrates are the major source of energy for the horse. However, the carbohydrates are a big family including a great variety of components from the simple sugars to the more complex starches and celluloses. The different carbohydrates are digested either enzymatically in the small intestine or fermented by intestinal microbes mainly in the hind-gut.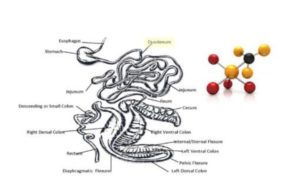
Small intestinal digestion
In the small intestine, sugar and starch is enzymatically broken down to simple sugars and absorbed to the blood as glucose (blood sugar). Here it is transported to the liver, muscles and other organs for energy, stored as glycogen or stored as body fat. The level of blood glucose is strictly regulated by insulin. Most horses have little problems with the absorption and regulation of glucose, however there are horses and ponies that are insulin resistant and have problems with the regulation of their blood glucose. For these horses, sugar and starch in the ration must be kept as low as possible.
In normal rations, it is mainly the starch from grains in compound feeds that can be a problem. Barley and maize contain about 500 grams/kg, while oats contain about 350 grams/kg. In compound feeds, the starch content varies from about 140 grams/kg and up to 450 grams/kg. If your horse has problems tolerating too much starch in the ration, you should choose one of the low-starch feeds. For normal healthy horses it is recommended to not give more than 0,4 kg cereal-based compound feeds per 100 kg body weight per meal. This means max 2 kg per meal for a 500 kg horse.
Fermentation in the hind-gut
The fibers, mainly cellulose and hemicellulose, are fermented by microbes in the caecum and colon. This leads to production of volatile fatty acids, mainly acetic acid, propionic acid and butyric acid. These acids are absorbed and readily utilized for energy or stored as fat. The propionic acid can also be converted to glucose in the liver. The volatile fatty acids that are produced in the hind-gut do not lead to any problems for the horse and are readily absorbed and utilized. Therefore, forage and other fibrous feeds should make up as big part of the horse’s ration as possible. This is also vital for normal fill and transport in the gut.
Pegus Diet Planning
When Pegus composes your rations, we can see at all times how much sugar, starch and fiber the ration contains. In this way, we can adjust the ration to be as optimal as possible for each individual horse. In addition, we also see the content and balance for the other required nutrients. Insuring a balanced ration is recommended
Free Phone Helpline
R.O.I.= 1800-378463
UK = 0800 011 4182







