B-vitamins are a group of 8 water soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism. They cannot be produced by the body itself, but can be produced by bacteria, fungi and plants. In the horse, microorganisms in the gut (mainly the hind gut) are capable of synthesizing B-vitamins. Equine nutrient requirements have only been established for thiamin (B1) and riboflavin (B2). In this article we will look at the function, dietary sources and requirements for thiamin (vitamin B1).
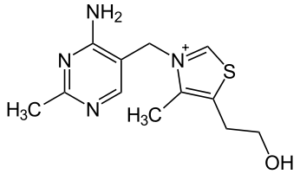
Function
Thiamin is a sulfur-containing vitamin that plays vital roles in the energy metabolism. It is needed when carbohydrates, fats and proteins are used for production of the high energy compound ATP and for the production of pentose sugars (ribulose) needed for the production of the nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
Dietary sources
Thiamin is found in relatively high concentrations in cereal grains and byproducts (see table).
Corn 3.5 mg/kg DM
Oats 5.2 mg/kg DM
Wheat 5.5 mg/kg DM
Barley 5.7 mg/kg DM
Wheat bran 8.0 mg/kg DM
Wheat middlings 12.0 mg/kg DM
Rice bran 23.0 mg/kg DM
Brewer’s yeast 95.2 mg/kg DM
These concentrations of thiamin in feeds will decrease during storage.
Thiamin is included in most concentrate mixtures for horses (10 – 20 mg/kg) and in vitamin supplements.
Requirements
The NRC 2007 gives requirements for thiamin for horses (see table).
Maintenance 0.06 mg/kg body weight
Light exercise 0.06 mg/kg body weight
Moderate exercise 0.113 mg/kg body weight
Heavy exercise 0.125 mg/kg body weight
Very heavy exercise 0.125 mg/kg body weight
Pregnant mares 0.06 mg/kg body weight
Lactating mares 0.075 mg/kg body weight
Growing horses 0.075 mg/kg body weight
Deficiency
Beriberi is the classical deficiency symptom of thiamin deficiency. Anorexia, bradycardia, muscle fasciculation and ataxia have been reported in horses with thiamin deficiency. Deficiency symptoms in horses fed typical feed ingredients have not been reported.
Toxicity
As thiamin is a water-soluble vitamin, excess intake will be excreted in the urine. Thiamin toxicity in horses has never been reported.
Pegus PC-Horse
PC-Horse calculates requirements for thiamin individually for each horse according to the NRC recommendations. It has also included values for thiamin (vitamin B1 ) in all feed tables. When composing rations for your horse using PC-Horse, you will always be able to control that your horse’s thiamin intake is in accordance with its requirements (all versions except the Mini-version).
For further information on feeding issues or diet planning, visit www.pegus.ie or contact the free phone helpline R.O.I.= 1800-378463 UK = 0800 011 4182








